My blog, AI Meets Creativity: How AI PPT Maker Elevates Your Content, is a detailed narration of the table below:-
| Feature/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Tool Name | AI PPT Maker |
| Purpose | To automatically generate professional PowerPoint presentations using AI models like ChatGPT and DeepSeek. |
| Input Options | - Text input - File upload - YouTube links - Voice commands - Web URLs |
| Output Format | Editable PowerPoint (PPT) files ready for download and customization |
| Customization | - Choose language - Presentation style (Professional, Creative, etc.) - Content depth (Basic to Advanced) |
| Speed & Efficiency | Generates full presentations within seconds, saving hours of manual work |
| AI Technology Behind It | Powered by ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and other LLMs for accurate and relevant content generation |
| Creative Use Cases | - Educational Slides - Business Proposals - Marketing Decks - Content Creators & Influencers - Academic Projects |
| Benefits Over Traditional PPTs | - Instant results - Zero design skills required - Error-free structure - Consistent formatting |
| Ease of Use | Designed with a clean, intuitive interface; perfect for both beginners and pros |
| Accessibility | Fully web-based; works on any device with a browser |
| Free vs Paid | - Free tier for basic use - **Premium features** for export options, branding, or advanced slide templates |
| Productivity Boost | Speeds up ideation, slide creation, and visual formatting—letting users focus on content, not layout |
| Smart Slide Structuring | Automatically organizes content into intro, key points, visuals, and conclusion—just like a real presentation expert |
Introduction
- AI PPT Maker is used to create Presentations within minutes and generate AI content on particular given topics.
- Now there is no need to spend hours sitting in front of the computer screen for formatting presentations in tedious conventional manner.
- The AI tool, AI PPT maker will do it for you. All you have to do is, enter the name of the topic on which you want the presentation, and AI content will be generated and also organized in the form of a PPT on the platform.
- You can access the PPT in the form of PowerPoint, Docx, or a PDF file.
- Ready-to-use templates are freely available on the platform, making the presentations more accurate and attractive. The presentations are well-organized in the form of pages with well defined point structure and attractive headings.
- The templates use Symbols, Elements, Projects, Brands and Designs to execute the automated AI presentations.
- You can enter the text of the topic for which you want the presentation. You can either enter the text of the topic for which you want the presentation or, upload a PPT of the file, enter a URL of the PPT or upload a YouTube video of the topic, or enter a voice of the voiceover of the topic, or the platform for which you want to create a presentation.
- There is a feature for creating your presentation as well as using the existing templates. Now there is no need to spend hours at work creating presentations by professionals.
- You only have to know the use of the AI tool and within a matter of minutes, the PPT will be prepared.
- The time and effort of manually organizing and designing the slides are saved, as AI can instantly generate a polished presentation, allowing you to focus on refining your message rather than formatting.
- The look and feel of the presentations are very professional and consistent making them easier to follow. The presentation created by the AI tool extracts the key points ensuring that your presentation is compact and impactful.
The need for AI PPT Maker
- For content creators, SEO optimization and accessibility, tools like AI PPT Maker can be a great asset as you could integrate these automated presentations into blogposts or educational content to offer dynamic visuals.
- The AI tool creates Presentations which pitch an Idea or explain a strategy, well crafted presentations help convince stakeholders and keep audiences engaged.
- Executives and managers rely on the presentations created by the AI tool, to analyze data, compare options and make informed decisions.
- Businesses use polished slides to showcase progress, reports and proposals to investors, clients and partners.
- The AI presentation tools are enhanced with the use of audiences. The content generated will get enhanced and updated with the time to come in the future.
- The AI tool has a lot of scope in companies and organizations as it saves time and effort.
- The proper and regular use of this AI tool, will make the lives of the professional much more easier and also will enhance their reputation in their respective organizations.
- Hence the use of this AI tool for creating presentations is highly recommended.
Conclusion
- AI is a helpful partner, not a full replacement. It can speed up work and organize things well, but your creativity is still important to make presentations engaging and personal.
- Use AI tools to handle design and save time, but don’t let them take away your real voice. Let AI build the structure, and you add the story and human touch.
How to use AI PPT Maker?
AI Meets Creativity: How AI PPT Maker Elevates Your Content i.e. the process of using AI PPT Maker is as follows:-
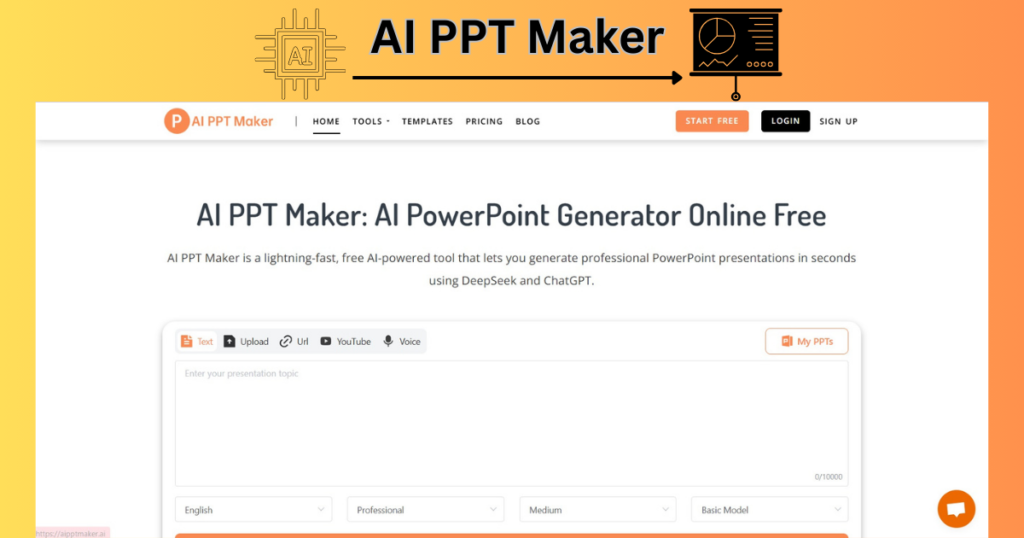
- Go to https://aipptmaker.ai/.
- You will navigate to the following page—>
- Press—>Sign Up.
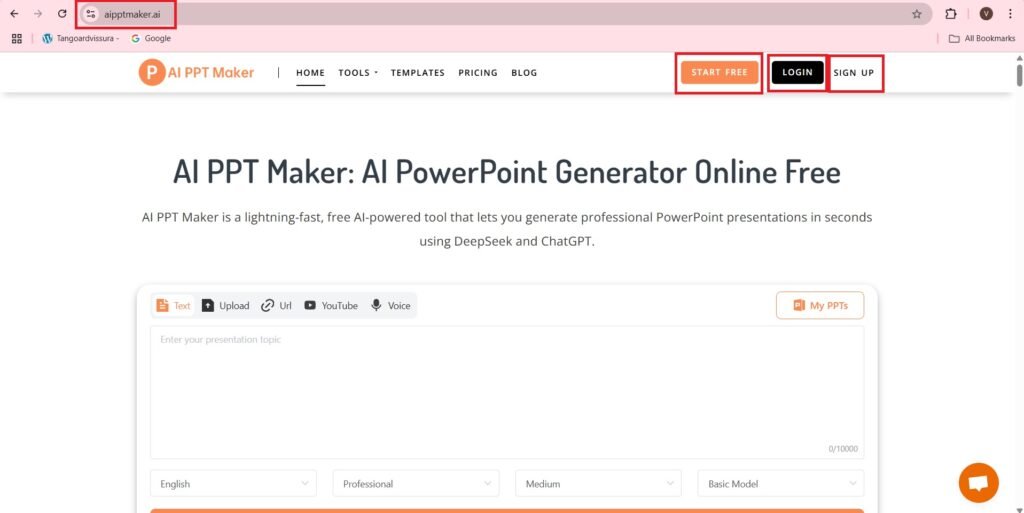
- Register with your email, and entering a password.
- Or Sign In with your Google Account.

- Choose an account—>
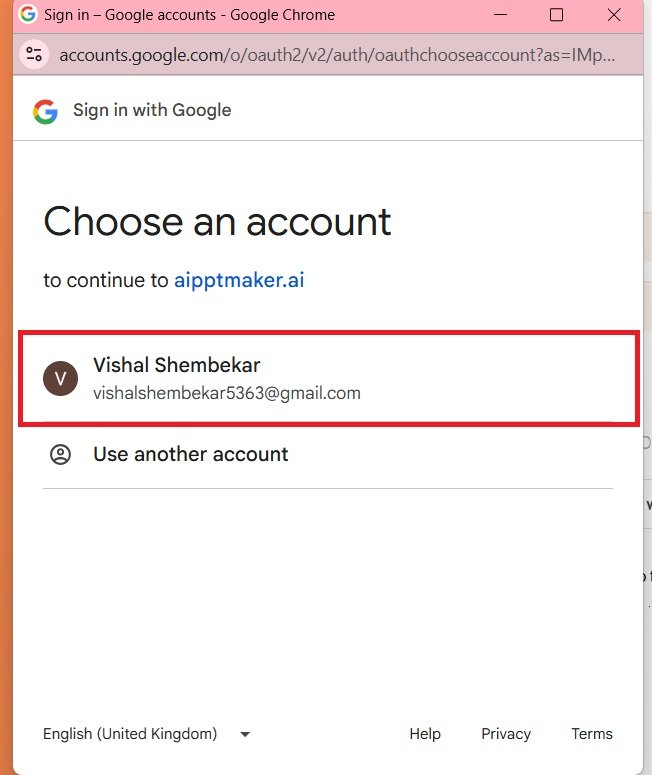
- Continue—>
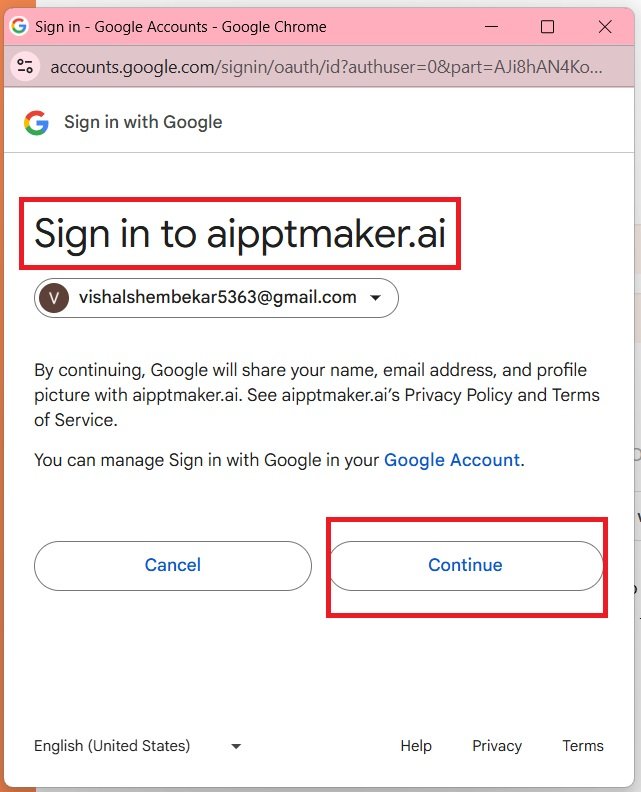
- You will navigate to the dashboard,
- Press—>Create with AI.
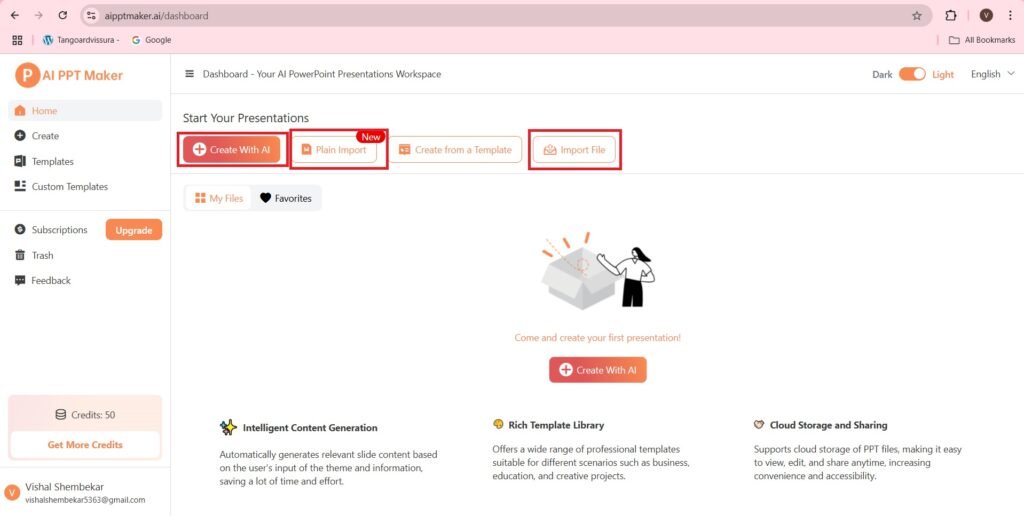
- Enter text that is to be used to generate the PPT.
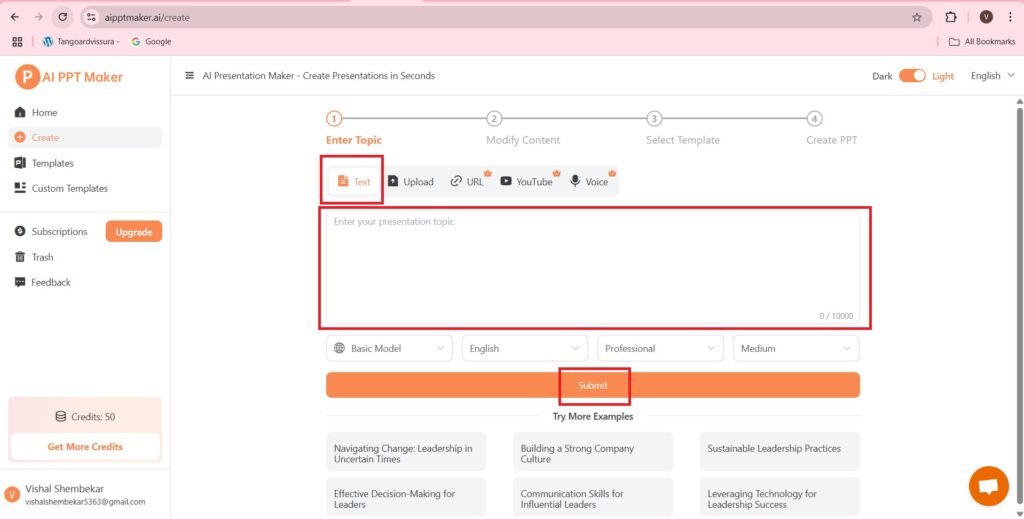
- The text I am entering is, “Software Testing”. You can enter any topic that you want.
- Press—>Submit.
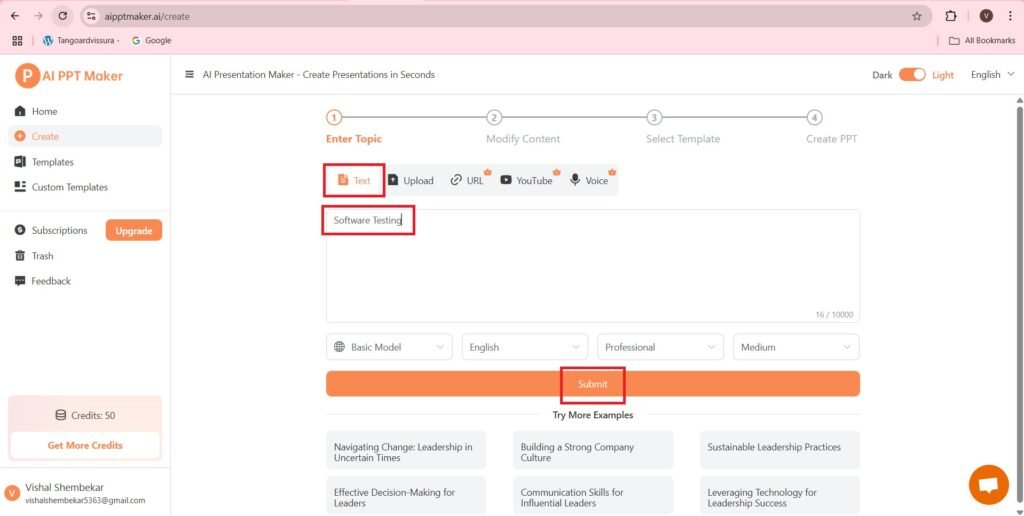
- The content generated is as follows:-
- The content is editable, i.e. you can modify the content as and when needed.
- Press—>Select Template
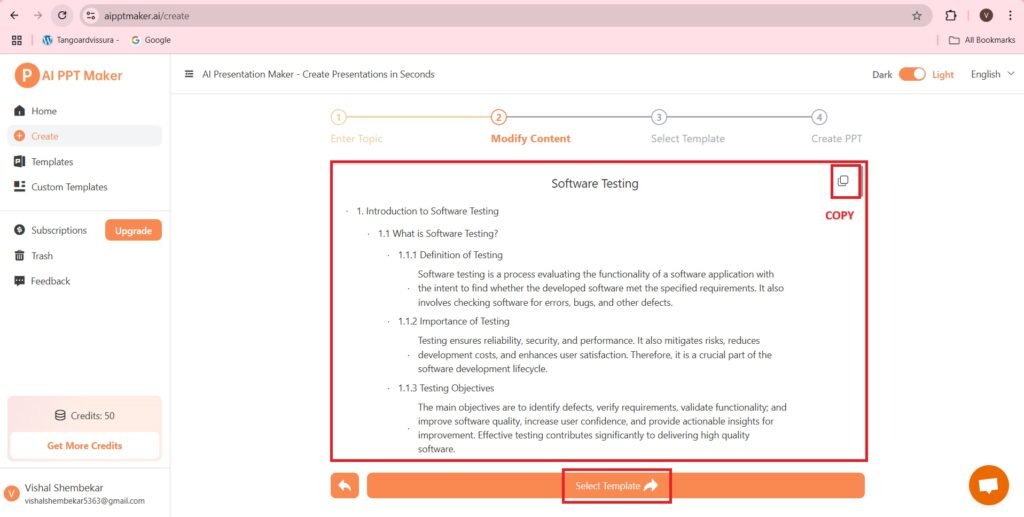
- The content is copy pasted as follows:-
- Software Testing
- 1. Introduction to Software Testing
- 1.1 What is Software Testing?
- 1.1.1 Definition of Testing
- Software testing is a process evaluating the functionality of a software application with the intent to find whether the developed software met the specified requirements. It also involves checking software for errors, bugs, and other defects.
- 1.1.2 Importance of Testing
- Testing ensures reliability, security, and performance. It also mitigates risks, reduces development costs, and enhances user satisfaction. Therefore, it is a crucial part of the software development lifecycle.
- 1.1.3 Testing Objectives
- The main objectives are to identify defects, verify requirements, validate functionality; and improve software quality, increase user confidence, and provide actionable insights for improvement. Effective testing contributes significantly to delivering high quality software.
- 1.2 Why is Software Testing Important?
- 1.2.1 Identifying Defects Early
- Early detection reduces costs and prevents potential customer dissatisfaction; fixing a bug in the testing phase is less expensive than fixing it post-release. Therefore, early testing is highly beneficial.
- 1.2.2 Ensuring Software Quality
- Testing verifies compliance with requirements, confirms that all functionalities work as expected, and helps to meet customer expectations. Quality assurance through testing is critical for software success.
- 1.2.3 Reducing Development Costs
- Finding and fixing defects during testing minimizes rework, saves time, and lowers overall project expenses. Cost-effective testing strategies are vital for efficient development.
- 1.3 SDLC and Testing
- 1.3.1 The Role of Testing in SDLC
- It is an integral part of the SDLC, ensuring the software meets standards at each stage. Testing should occur from the beginning to the end of development.
- 1.3.2 Different Phases and Corresponding Tests
- Requirement analysis involves understanding and testing user needs; design phase includes unit testing and integration testing; deployment requires system and acceptance testing. Each phase requires different testing methods.
- 1.3.3 Benefits of Early Testing Involvement
- Involving testing early can catch defects from inception, reduce late-stage rework and saves both time and costs. Therefore, early involvement is invaluable.
- 2. Types of Software Testing
- 2.1 Black Box Testing
- 2.1.1 Definition and Characteristics
- Black box testing involves testing software without knowledge of its internal structure. It mainly focuses on input and output relationships.
- 2.1.2 Common Black Box Techniques
- Equivalence partitioning divides inputs into valid/invalid groups. Boundary value analysis tests at edges of input domain. Decision table testing covers conditional logic.
- 2.1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages
- Easy to implement, tests functionality without bias. But it can have limited test coverage. It also may not find hidden or internal defects.
- 2.2 White Box Testing
- 2.2.1 Definition and Characteristics
- White box testing involves testing software with deep knowledge of its structure. It requires understanding of the internal code and design.
- 2.2.2 Common White Box Techniques
- Statement coverage checks every line of code. Branch coverage tests all possible outcomes. Path coverage ensures every path is executed.
- 2.2.3 Advantages and Disadvantages
- Maximizes test coverage, finds hidden errors, optimizes code. However, it can be complex, expensive, and requires skilled testers. Therefore, choose wisely.
- 2.3 Gray Box Testing
- 2.3.1 Definition and Characteristics
- Gray box testing is a hybrid approach, with partial knowledge of internal structure. Testers have access to design documents, and algorithms.
- 2.3.2 Examples of Gray Box Techniques
- Matrix testing defines input combinations. Regression testing checks for new errors. Pattern testing uncovers hidden patterns.
- 2.3.3 Use Cases for Gray Box Testing
- Effective for security testing, integration testing, and database testing. It balances the advantages of both white box and black box testing. It is highly versatile.
- 2.4 Other Testing Types
- 2.4.1 Functional Testing
- Functional testing evaluates if functions match specifications. It may include Unit testing and Integration testing components. These assure the software operates properly.
- 2.4.2 Non-Functional Testing
- Non-Functional testing include performance, security and usability testing. They judge characteristics rather than specific functions and are essential for overall quality assessment.
- 2.4.3 Performance Testing
- Performance testing assesses speed, stability and scalability under load; Key metrics include response time and throughput. Performance tests pinpoint bottlenecks and ensure efficiency.
- 3. Testing Levels
- 3.1 Unit Testing
- 3.1.1 Definition and Purpose
- Testing individual software components or modules in isolation. Aims to verify each unit performs as designed. Helps identifying errors early!
- 3.1.2 Who Performs Unit Testing?
- Typically done by developers; They write tests to check their code, ensuring it meets design specifications. Developer driven, and code focused.
- 3.1.3 Benefits of Unit Testing
- Early detection of defects, simplifies debugging, facilitates code reuse. Unit tests serve as documentation and reduce integration errors. Therefore, early detection is key!
- 3.2 Integration Testing
- 3.2.1 Definition and Purpose
- Combining and testing multiple units as a group; Checks interactions and data flow between components. Integration testing is crucial for system reliability.
- 3.2.2 Types of Integration Testing
- Big Bang approach integrates all modules at once; Top-down and bottom-up approaches integrate incrementally. Choosing the right strategy depends on projects size and components complexity.
- 3.2.3 Challenges in Integration Testing
- Complex interfaces, data inconsistencies, coordinating multiple testers. Thorough planning and communication among teams are essential. Therefore, planning and communication is key.
- 3.3 System Testing
- 3.3.1 Definition and Scope
- Testing the entire software system as a whole. Validates if system meets all requirements and specifications. Simulates real-world conditions.
- 3.3.2 Common System Testing Types
- Functional testing, performance testing, security testing. Usability and reliability testing; These ensure comprehensive system validation.
- 3.3.3 Importance of System Testing
- Verifies end-to-end functionality, ensures compatibility, increases user confidence. System testing ensures the reliability and stability of the software system. Therefore, reliability builds confidence!
- 3.4 Acceptance Testing
- 3.4.1 Definition and Purpose
- Conducted by end-users to determine whether the software meets their needs. Formal approval process before software can be deployed. Therefore, this is formal user approval!
- 3.4.2 Types of Acceptance Testing
- User acceptance testing (UAT), beta testing, operational acceptance testing. Each catering to diffrent stakeholder perspectives. Diverse perspectives ensure broad system validation.
- 3.4.3 Key Objectives of Acceptance Testing
- Validates usability, confirms system meets business requirements, ensures user satisfaction. Acceptance testing directly assures user and bussiness alignment. Therefore, alignment leads to higher satisfaction!
- 4. Testing Techniques
- 4.1 Test Case Design
- 4.1.1 What is a Test Case?
- A set of conditions and steps to verify a specific feature or functionality. Test cases should be detailed, repeatable, and cover different scenarios. Therefore, detail creates repeatability.
- 4.1.2 Components of a Test Case
- Test case ID, description, preconditions, steps, expected result, and actual result. Each component is vital for structured testing. Having more details can ensure thorough testing.
- 4.1.3 Test Case Prioritization
- High-priority tests cover critical functionalities. Medium-priority tests cover important features. Low-priority tests cover edge cases and minor functions. Therefore, prioritize tasks properly.
- 4.2 Test Data Generation
- 4.2.1 Importance of Test Data
- Realistic data simulates real-world scenarios, improving test coverage. Invalid data identifies edge cases and vulnerabilities; and Good data enables robust test result.
- 4.2.2 Techniques for Generating Test Data
- Manual data creation, automated data generation, copying from production. Therefore, diverse data sets for comprehensive testing. Diversity ensures thoroughness.
- 4.2.3 Data Masking and Anonymization
- Protect sensitive information, maintain compliance, preserve data integrity. Mask sensitive data for security and privacy. Protecting information is a must.
- 4.3 Test Environment Setup
- 4.3.1 Key Elements of a Test Environment
- Hardware, software, network configurations, and databases. Ensure the setup closely mimics the production environment. Precise simulation is vital for valid result!
- 4.3.2 Configuration Management
- Track changes, maintain consistency, ensure reproducibility, implement version control, use automation tools. Effective configuration management limits the chance of errors. Manage them well!
- 4.3.3 Automation in Test Environment Setup
- Use scripts, tools, and CI/CD pipelines to automate setup and deployment. This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and speeds up testing. Speed, reduce manual labor and reduce errors!
- 5. Defect Management
- 5.1 Defect Life Cycle
- 5.1.1 Stages of a Defect’s Life
- New, assigned, open, fixed, retested, closed. Each stage represents a step in resolution management. It is important to have steps.
- 5.1.2 Importance of Tracking Defects
- Provides visibility, enables analysis, improves quality. Tracking defects is crucial for software assessment! You can improve by tracking and reviewing!
- 5.1.3 Defect Reporting Tools
- Jira, Bugzilla, Mantis; Tools used to log, track, and manage defects. Defect tools help log and track.
- 5.2 Defect Reporting
- 5.2.1 Components of a Defect Report
- ID, summary, description, steps to reproduce, severity, priority, and assigned tester. Precise reporting aids effective defect resolution. Therefore it makes solving defect easier.
- 5.2.2 Writing Effective Defect Reports
- Be clear, provide context, include attachments (screenshots, logs). Good defect reports ease debugging!
- 5.2.3 Communicating Defects Effectively
- Collaborate with developers, participate in triage meetings, and follow up on resolutions. Effective communication speeds up resolution. Effective communication limits the resolution time.
- 5.3 Root Cause Analysis
- 5.3.1 Identifying the Underlying Cause
- Dig deeper to find the real reason for the defect. Prevent recurrence by addressing the root cause. Why and how did this happen?
- 5.3.2 Techniques for Root Cause Analysis
- 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, Pareto analysis. Use various tools to identify the root cause. Utilizing root causes can help make significant improvements!
- 5.3.3 Preventing Defect Recurrence
- Implement code reviews, improve testing strategies, train developers. Proactive measures limit defect recurrence. Take proactive measures right away.
- 6. Test Automation
- 6.1 Introduction to Test Automation
- 6.1.1 What is Test Automation?
- Using tools and scripts to execute tests automatically. Automates processes, reduces manual efforts, speeds up testing. It is a great tool!
- 6.1.2 Benefits of Test Automation
- Faster execution, improved accuracy, increased coverage, continuous testing. The benefits include accuracy and faster execution!
- 6.1.3 When to Automate
- Automate repetitive tests, regression tests, performance tests. Automate when tasks are monotonous. Automate repetitive tasks!
- 6.2 Automation Tools and Frameworks
- 6.2.1 Popular Automation Tools
- Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, Appium. Tools to automate web, API, and mobile apps. Select the appropriate tools for the tasks!
- 6.2.2 Choosing the Right Tool
- Consider project requirements, skills, costs, and scalability. Select tools based on your projects needs. Select a tool that suits your needs!.
- 6.2.3 Test Automation Frameworks
- Linear, modular, data-driven, keyword-driven, hybrid. Select based on needs!
- 6.3 Implementing Test Automation
- 6.3.1 Building a Test Automation Strategy
- Define scope, objectives, metrics, and prioritize test cases. A clear strategy is key to automation success. Ensure you have a clear strategy.
- 6.3.2 Writing Automated Tests
- Follow coding standards, use descriptive names, include comments. Clear, maintainable tests improve reliability. Test with maintainability and clarity!
- 6.3.3 Continuous Integration
- Integrate automated tests into CI/CD pipelines for continuous feedback. Early feedback improves efficency and reduces work! Integration is key!.
- 7. Future Trends in Software Testing
- 7.1 AI and Machine Learning in Testing
- 7.1.1 Enhancing Testing with AI
- Predictive analysis, automated test case generation, intelligent defect detection. AI is transforming software testing. AI’s new capabilities should be incorporated!.
- 7.1.2 Opportunities and Challenges
- Improved efficiency, reduced costs, scalability; Data dependency, bias, complexity. Every coin has two sides!
- 7.1.3 The Future of AI in Testing
- More sophisticated AI solutions, wider adoption, personalized testing. Prepare for the rise of AI in testing. Future trends should be monitored to keep up pace!
- 7.2 Shift Left Testing
- 7.2.1 What is Shift Left Testing?
- Moving testing earlier in the development lifecycle. Reduces costs, prevents defects, improves collaboration. Test early to avoid setbacks.
- 7.2.2 Benefits of Shift Left Testing
- Early defect detection, better quality, faster feedback loops. Early awareness can positively influence progress and outcomes!
- 7.2.3 Implementing Shift Left
- Involve testers early, integrate testing into development, use automation. Bring testing to the forefront. Make sure it is included.
- 7.3 DevOps and Continuous Testing
- 7.3.1 DevOps and Testing
- Integrating testing into DevOps practices for continuous delivery. Testing should be integrated into new systems and pipelines. Integrate!
- 7.3.2 Continuous Testing Framework
- Automated tests, CI/CD pipelines, continuous feedback loops. Build a framework to support constant testing. Build it to support consistency.
- 7.3.3 The Impact of DevOps on Testing
- Faster release cycles, improved quality, increased collaboration. The collaboration aspect is key.
- On Pressing ‘Select Template’, You will navigate to the following page:-
- Press—>Generate PPT.
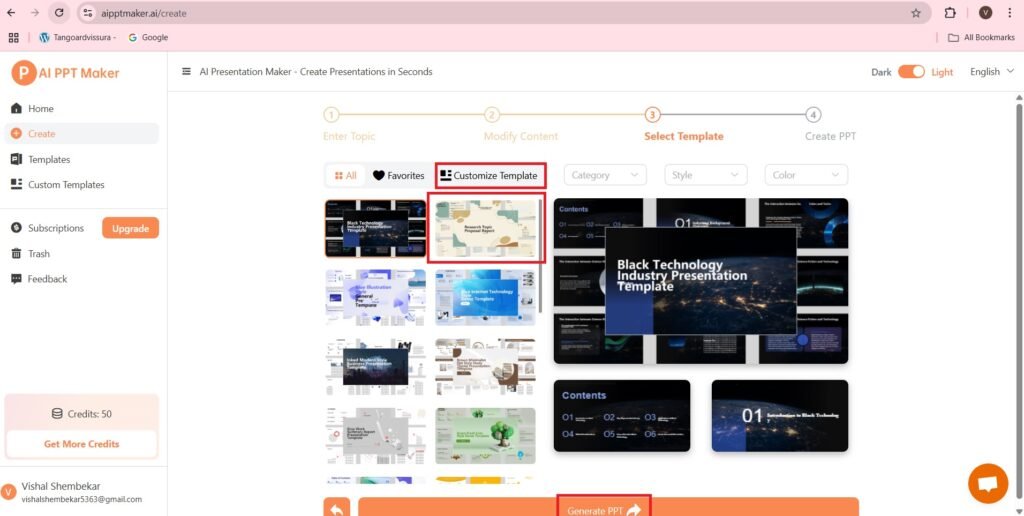
- Now Customize the template—>
- Press—>Generate PPT
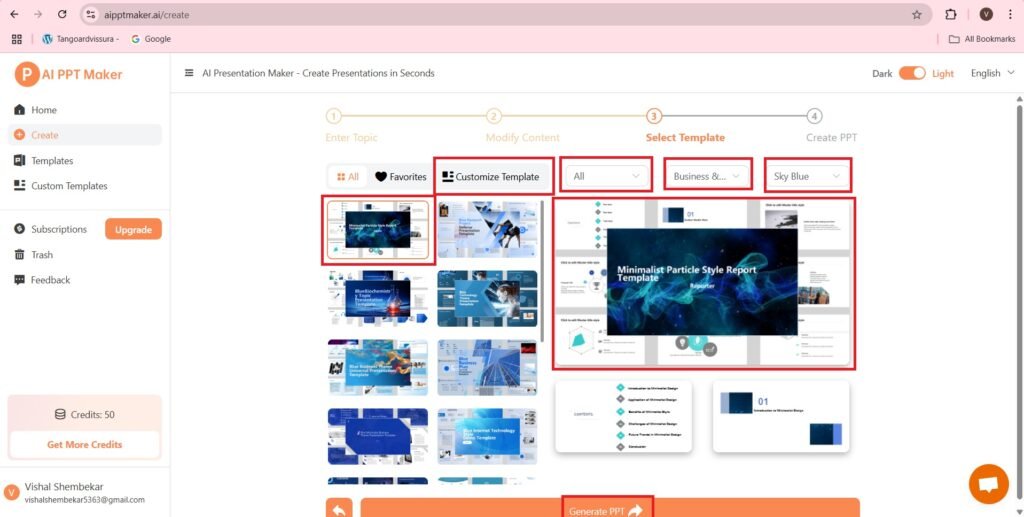
- The process needs to be quick, to generate the PPT, else it will not be generated.
- I have not taken the above template shown in the screenshot, as I have redone the process with a different template, and generated a PPT on ‘Software testing’. The content generated through the process may also vary from the above copied content. But I will show you the new PPT.
- The PPT is as follows:-
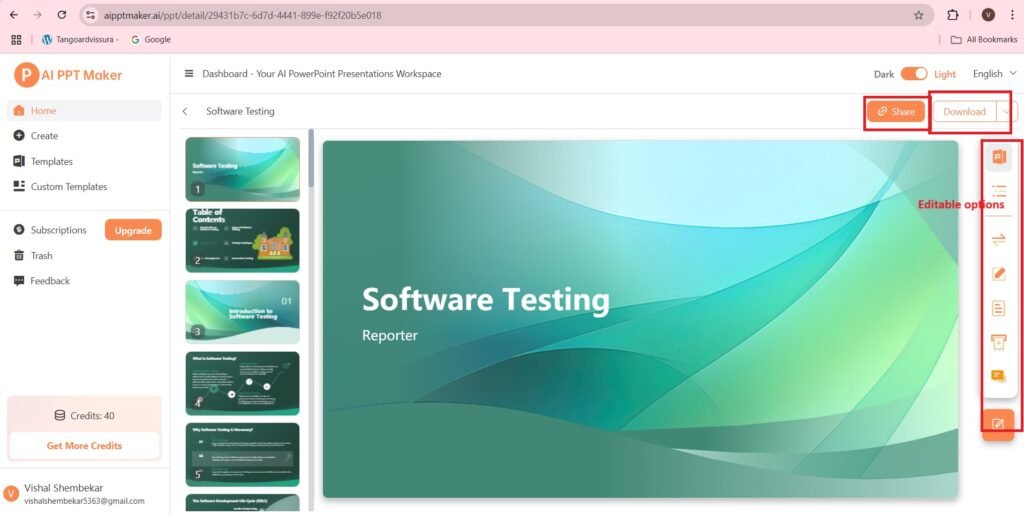
- The PPT generated is as follows:-
 Loading…
Loading…
- Navigate to the Home Page—>
- Press—>Plain Import
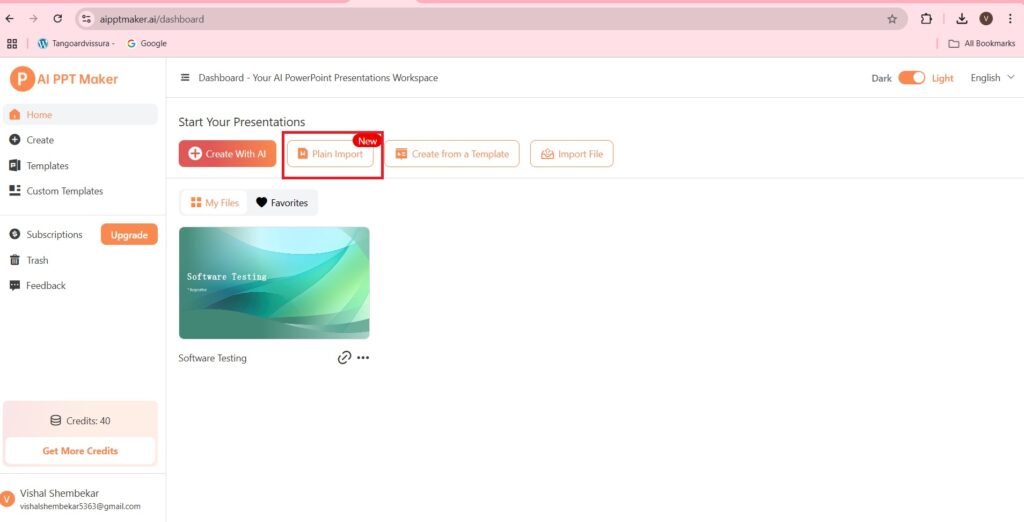
- The process remains the same as shown before. I am uploading the following Word File(Docx file).
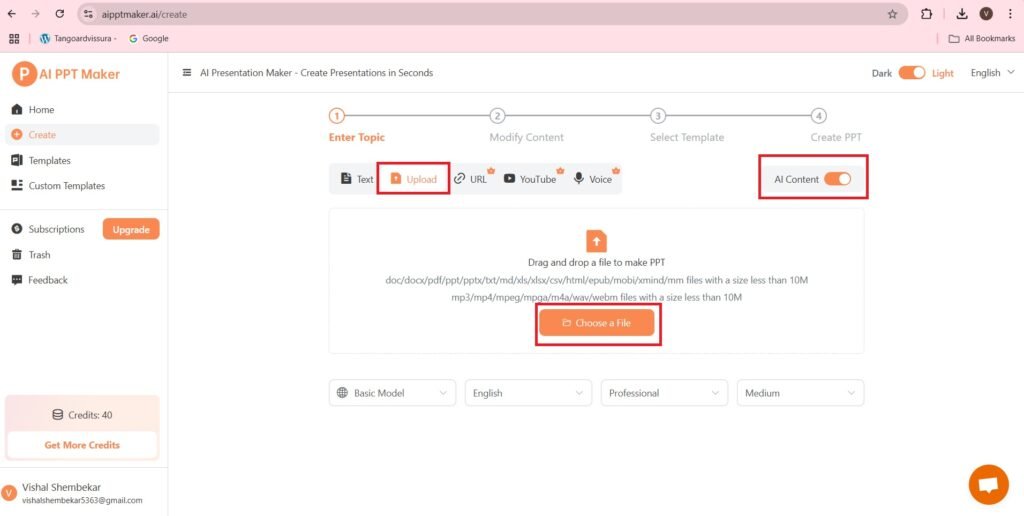
- After uploading the above Word File(Docx document) on the above Upload section, and following the process of generating PPT, we get the following result—>
- The content is generated as follows:-
- Software Testing: An Overview
- 1 Introduction to Software Testing
- 1.1 What is Software Testing?
- 1.1.1 Defining Software Testing
- Software testing is a process of evaluating software functionality to find defects; it confirms the software meets specified requirements and ensures it performs as expected, providing confidence in its reliability.
- 1.1.2 Why is Software Testing Important?
- Effective testing leads to higher quality software, reduced development costs, and increased user satisfaction; it also minimizes risks related to software failures, enhancing an organization’s reputation.
- 1.1.3 The Software Testing Lifecycle
- The testing lifecycle includes planning, analysis, design, implementation, execution, and conclusion; each phase plays a vital role in identifying and addressing potential issues early on.
- 1.2 Common Types of Software Testing
- 1.2.1 Black Box Testing
- Black box testing evaluates software without knowledge of the internal code structure, focusing on inputs and outputs; it emulates the user experience.
- 1.2.2 White Box Testing
- White box testing examines the internal code structure and logic, involving code coverage and path testing; therefore, developers frequently perform white box testing.
- 1.2.3 Gray Box Testing
- Gray box testing combines elements of both black and white box testing, offering partial knowledge of internal structures; this helps create targeted test cases.
- 1.3 The Benefits of Comprehensive Testing
- 1.3.1 Increased Reliability
- Thorough testing identifies bugs and vulnerabilities, ensuring software is reliable and performs consistently under various conditions; this enhances user confidence.
- 1.3.2 Reduced Maintenance Costs
- Early detection of defects reduces the cost of rework and future maintenance; fixing issues early minimizes disruption and lowers long-term expenses.
- 1.3.3 Enhanced User Satisfaction
- High-quality, well-tested software enhances user experience, increasing user satisfaction and loyalty; it builds a positive reputation for the software product.
- 2 Unit Testing
- 2.1 What is Unit Testing?
- 2.1.1 Definition of Unit Testing
- Unit testing involves testing individual components or modules of software in isolation; it aims to verify their correct functionality separately.
- 2.1.2 Goals of Unit Testing
- The primary goal is to ensure each unit of the software performs as designed; it also helps to identify and rectify defects early in the development cycle.
- 2.1.3 Unit Testing Frameworks
- Popular frameworks such as JUnit (Java), NUnit (.NET), and pytest (Python) support unit testing; these frameworks provide tools and structure for creating and running tests.
- 2.2 The Unit Testing Process
- 2.2.1 Writing Test Cases
- Test cases should cover all possible scenarios, including valid and invalid inputs, boundary conditions, and error handling; high-quality test cases are critical to the effectiveness of unit testing.
- 2.2.2 Executing Unit Tests
- Unit tests are typically automated and run as part of the build process; this ensures any newly introduced bugs are quickly identified.
- 2.2.3 Analyzing Test Results
- Analyzing the results of unit tests provides valuable feedback to developers; it helps them understand where the code is failing and what needs to be fixed.
- 2.3 Best Practices for Unit Testing
- 2.3.1 Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- TDD involves writing tests before writing the code; this forces developers to think about requirements and design before implementation.
- 2.3.2 Keeping Tests Independent
- Each unit test should be independent of other tests; this ensures that failures are isolated and easier to diagnose.
- 2.3.3 Automating Unit Tests
- Automating unit tests as part of the CI/CD pipeline ensures continuous feedback; faster feedback allows quicker resolution of issues and improves overall development efficiency.
- 3 Integration Testing
- 3.1 What is Integration Testing?
- 3.1.1 Definition of Integration Testing
- Integration testing verifies that combined units or modules work together as expected; it focuses on the interfaces and interactions between components.
- 3.1.2 Purpose of Integration Testing
- The primary purpose is to detect defects when integrating different software modules; testing how data is passed between modules, and if the modules interact correctly is imperative.
- 3.1.3 Types of Integration Testing
- Big Bang, top-down, bottom-up, and sandwich integration testing are common approaches; selecting the appropriate strategy depends on project size and architecture.
- 3.2 The Integration Testing Process
- 3.2.1 Planning Integration Tests
- Plan tests by identifying the modules to be integrated and defining test scenarios focused on their interactions; the plan should outline milestones, resources, and schedules.
- 3.2.2 Performing Integration Tests
- Executing the tests and logging the outcomes, examining how modules perform combined tasks when data is exchanged, and identifying discrepancies is crucial.
- 3.2.3 Resolving Integration Issues
- Address integration defects by prioritizing fixes and retesting modules after modifications; confirm that fixes do not introduce new issues in other parts.
- 3.3 Key Strategies for Successful Integration
- 3.3.1 Continuous Integration
- Continuous Integration involves automating the integration of code changes from multiple developers; it detects integration issues early.
- 3.3.2 Using Mock Objects
- Mock objects simulate the behavior of real components, facilitating testing when components are unavailable.
- 3.3.3 Early and Frequent Integration
- Integrating code frequently detects integration issues early; it avoids large, problematic integrations later in the development cycle.
- 4 System Testing
- 4.1 What is System Testing?
- 4.1.1 Definition of System Testing
- System testing validates that the entire system meets specified requirements; it tests the system as a whole, rather than individual components.
- 4.1.2 Scope of System Testing
- It covers both functional and non-functional requirements, including performance, security, and usability; therefore confirming the system’s overall quality is imperative.
- 4.1.3 Types of System Tests
- Performance testing, security testing, and usability testing are examples of system test segments; each focusing on distinctive elements of the system.
- 4.2 The System Testing Process
- 4.2.1 Creating System Test Cases
- Test cases should cover all aspects of the system, using requirement specifications for direction; create cases that span all functionalities for extensive coverage.
- 4.2.2 Executing System Tests
- Simulate real-world conditions and user scenarios to detect defects; also observe system behavior under a range of parameters.
- 4.2.3 Reporting and Tracking Defects
- Report any found defects with descriptive details and track their resolution; utilize bug tracking tools to control the fix process.
- 4.3 Ensuring Comprehensive System Coverage
- 4.3.1 Risk-Based Testing
- Focus testing efforts on areas with the highest risk; this method helps you allocate resources efficiently.
- 4.3.2 Test Data Management
- Manage the test data accurately in a way that can facilitate consistent and credible test cycles.
- 4.3.3 Automation in System Testing
- Automate regression tests to guarantee that bug fixes are sustained; automation helps you to regularly and promptly validate system stability.
- 5 Acceptance Testing
- 5.1 What is Acceptance Testing
- 5.1.1 Defining Acceptance Testing
- Acceptance testing ensures software meets business requirements; it determines if the software meets acceptance criteria.
- 5.1.2 Importance of User Involvement
- End-users, clients, and stakeholders are involved to validate the software; their input ensures that it meets their practical requirements.
- 5.1.3 Alpha vs. Beta Testing
- Alpha testing occurs in a controlled environment with internal testers; beta testing involves real users testing in real-world conditions, therefore gathering valuable user feedback.
- 5.2 The Acceptance Testing Process
- 5.2.1 Planning Acceptance Tests
- Outline specific test cases on business needs and acceptance standards; define the test environment that imitates the real use case.
- 5.2.2 Executing Acceptance Tests
- Execute planned tests using real-world scenarios and note results; record observations about user experience.
- 5.2.3 Gathering User Feedback
- Obtain feedback from users through reviews, surveys, or interviews; adjust the software based on user input.
- 5.3 Strategies for User Satisfaction
- 5.3.1 Clear Acceptance Criteria
- Clear acceptance criteria should be established and communicated; it sets straightforward expectations for the user community.
- 5.3.2 Providing Training and Support
- Give end users comprehensive training and help to navigate system; assist them with any problems they may have.
- 5.3.3 Iterative Testing and Feedback
- Gather and involve user feedback during the testing stages; this helps to continuously improve performance and satisfaction.
- 6 Conclusion
- 6.1 The Importance of a Robust Testing Strategy
- 6.1.1 Summary of Testing Types
- Summarizing unit, integration, system, and acceptance testing; and reinforcing their specific roles and importance in detecting defects.
- 6.1.2 Continuous Improvement Through Testing
- Testing should be a continuous process; adapt testing strategies based on feedback and evolving requirements.
- 6.1.3 Investing in Quality Assurance
- Highlighting the importance of resources for quality; this investment ensures reliability and user satisfaction.
- 6.2 Future Trends in Software Testing
- 6.2.1 AI and Machine Learning in Testing
- Exploring the use of AI and ML to automate test case generation; analyzing test results and predicting potential defects.
- 6.2.2 Shift-Left Testing
- Introducing testing early in the development cycle; encouraging testing involvement during design and coding.
- 6.2.3 Cloud-Based Testing
- Leveraging cloud-based resources for testing; providing scalability, flexibility, and cost savings for testing activities.
- 6.3 Thank You and Q&A
- 6.3.1 Acknowledgements
- Acknowledging contributors and resources used in the development of the presentation.
- 6.3.2 Open Forum for Questions
- Opening the floor for questions from the audience; and offering clarifications and detailed explanations in response to inquiries.
- 6.3.3 Final Remarks
- Providing closing remarks summarizing the core takeaways from the presentation; and reinforcing the importance of comprehensive software testing.
- Generating the PPT of the file is as follows:-
 Loading…
Loading…
Official Account of AI PPT Maker on LinkedIn

Mastering Presentations: Unleashing the Power of SlidesAI
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is AI PPT Maker?
AI PPT Maker is an AI-powered tool that helps you create professional PowerPoint presentations instantly using input like text, URLs, or voice.
Is AI PPT Maker free to use?
Yes, AI PPT Maker offers a free plan with basic features. Premium options may be available for advanced customization and export options.
How does AI PPT Maker generate presentations?
It uses advanced language models like ChatGPT and DeepSeek to understand your topic and generate well-structured slides accordingly.
What input formats does it accept?
You can generate slides from text, uploaded documents, URLs, YouTube videos, or even voice commands
Can I choose the presentation style or tone?
Yes! You can select options like Professional, Creative, or Educational, and adjust complexity (e.g., Basic, Medium, Advanced).
Do I need to download software to use it?
No, AI PPT Maker is completely web-based. You just need an internet connection and a browser.
Is my data safe on AI PPT Maker?
Yes, the platform claims to follow standard security practices, but it’s always wise not to upload confidential or sensitive information.
Can I edit the presentation after it’s generated?
Absolutely! You can download and edit the presentation in PowerPoint or Google Slides as needed.
Is it suitable for students and educators?
Definitely. It’s ideal for quick classroom slides, academic reports, or visual aids—saving hours of manual work.
How can I get started with AI PPT Maker?
Visit aipptmaker.ai, enter your topic or paste your content, choose your preferences, and click Generate.

